Bloom & Billets Continuous Casting Facilities (S.M.D) Pakistan Steel.
CONTINUOUS CASTING FACILITIES FOR LONG PRODUCTS (Blooms
& Billets).
Steel Making Department Pakistan Steel.
It
is essential to go through the characteristics of available production
facilities of an integrated steel mill, not only to get optimum benefits out
of it but also to put forward further improvement plan of production and
productivity in integration.
Blooms
and Billets are used to make long products. Before the advent of continuous
casting machines, the individually cast ingots in stationary moulds were used
to produce rolled Blooms and Billets. Now large size cast ingots are mainly
used to obtain forged parts.
Cast Bloom :
A
semi-finished long product of continuously cast steel of greater than 150 mm
square or rectangular cross-section. Blooms are used primarily as feedstock for
hot rolling to produce long heavy sections, rolled billets, piling, beams and
railway rails. A Bloom is a bigger sized Billet.
Cast Billet : A
semi-finished long product of continuously cast steel up to 150 mm square or rectangular cross-section
with round corners. A Billet is a smaller sized Bloom. Billets are used
primarily as feedstock for hot rolling or other processes to produce sections,
rods, seamless tubes, bars and wire products. Rolled bars can have
cross-section in the shape of squares, rectangles, circles, hexagons and
angles.
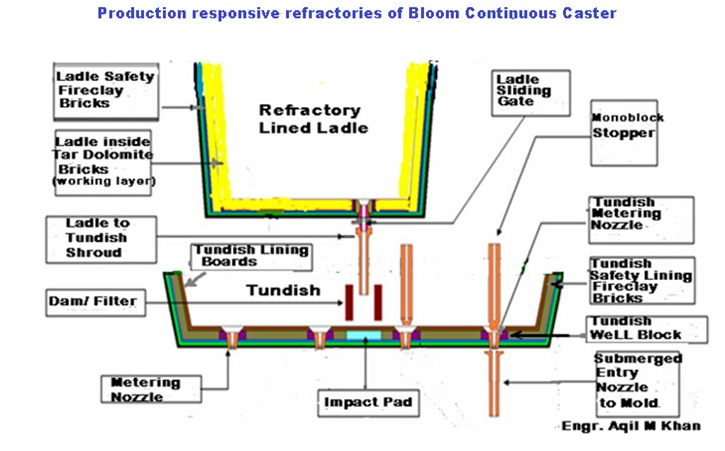
After tapping a batch of steel (heat) from LD Converter into
a refractory lined ladle, it is dispatched via an electrically driven Ladle car
to continuous casting bay/ aisle from where it is lifted by 180 Tonne overhead
crane to get it transported to the ladle treatment station for fine tuning of
chemical composition and adjustment of temperature as per required grade of
steel and then onward to the scheduled continuous casting machine ( Billet ,
Bloom or Slab ) .
 |
The ladle treatment station at Pakistan steel provided by Voestalpine
Austria has facilities of small ladle additions, cooling and nitrogen purging
from top where only high temperature heats can be treated and does not have any
temperature raising facility in case if it is lowered down due to prolong
holding .
4 - Strand Bloom Continuous Caster.
Bloom casters have been more widely installed by
integrated plants with higher production rate. Because the casting rate for the
larger Bloom cross-section is higher than for small billet sizes. Consequently
larger heat sizes of 100 – 400 tons can be cast with relatively fewer strands
and higher production rate in large integrated mills. Blooms sizes can vary
from 260x260mm to 320x 360 mm or even bigger sizes.
Continuous
caster’s speed varies and depends mainly on following factors:
- Cross-sectional
dimensions of moulds.
- Chemical composition
and temperature of Steel grade.
- Rate of heat transfer
in the mould.
- Strength of the
solidified casting crust.
- Methods of maintaining the track strand secondary
cooling.
As
per project, Pakistan steel is provided with a 4- Strand Bloom Continuous
Caster capable of casting 260 x 260 mm
cross section Blooms which are cut to length for subsequent reheating and rolling
into various sizes of Billets in 800 mm reversible Billet Mill.
A Butterfly type ladle turret holds the steel teeming ladles, weigh up to 130 tons. By means of the ladle turret, the steel teeming ladles are alternately rotated backward and forward into casting and charging position. This function ensures the uninterrupted operation of the continuous casting plant. While one ladle is emptied, a full ladle is provided on the other side. The ladle change time is only about one minute.
A Butterfly type ladle turret holds the steel teeming ladles, weigh up to 130 tons. By means of the ladle turret, the steel teeming ladles are alternately rotated backward and forward into casting and charging position. This function ensures the uninterrupted operation of the continuous casting plant. While one ladle is emptied, a full ladle is provided on the other side. The ladle change time is only about one minute.
Butterfly type turret has lifting and lowering lever arms on each side
driven by two hydraulic cylinders that can facilitate adjustment of ladle
height over tundish independently
on each side for better control of temperature in tundish.
A view of Butter Fly Type Ladle Turret of
Bloom Continuous Casting Machine under maintenance.
Continuous Casting Process:
Machine Preparation Before Commencement of Casting Operation:
To
initiate the continuous casting process the dummy bars are drawn from dummy bar
parking positions and are inserted through the secondary cooling sections into the
bottom of moulds to a recommended height and the
water cooling system of the continuous casting machine is turned on.
Dummy Bars.
Before the start
of casting process, the motors for the dummy bars storage unit are actuated to
lower the dummy bars down into the with drawer-straightening unit and are inserted,
passing through the secondary cooling sections into the bottomless moulds to a recommended height with
a detachable dummy
bar head. At the end of dummy bar
withdrawal operation, the dummy bar head is removed and the dummy bar returns
to the storage position and park there till next casting operation.
The
heat finishing time or ladle emptying time depends on cross sectional area of the
moulds, the number of strands ,
temperature and speed of casting and steel
grade.
The
filled steel ladle is transported via over head crane from ladle treatment
station onto the ladle turret of the casting machine and brought to the teeming
position above the tundish. The hydraulically operated slidegate of ladle is
opened to dispense the steel into the tundish.
A view of ladle slidegate dispensing the metal into
tundish at the commencement of continuous casting process.
The tundish distributes precisely the right amount
of liquid steel via monoblock stoppers and metering nozzles to water circulated
copper moulds. One of the key functions of tundish is to hold buffer stock of
metal to supply a continuous flow of liquid steel to the moulds during ladle
exchange.
The amount of super-heat contained in the
liquid steel has a profound effect upon the internal metallurgical quality of
the cast product (Blooms or Billets). The liquid steel temperature in the
tundish is therefore maintained within the range liquidus plus 150C.
IRON- CARBON DIAGRAME
Also
the effect of other alloying additions on liquidus temperature is taken into consideration
that varies as per required steel grade.
During continuous casting process the refractories of steel casting
ladle & tundish are exposed to heavy erosion and abrasion
action of molten steel and slag.
Also the oxygen pick up by molten metal from
atmosphere is a common phenomenon.
Therefore the quality of steel that comes out of
tundish does not remain the same as that poured from teeming ladle. The
inclusions of eroded refractory materials and the re-oxidation products are
always there which deteriorates the quality of cast steel in the mould.
Inclusions Preventive Measures in
Tundish :
-To prevent re-oxidation of metal from atmosphere
and to avoid loss of temperature in tundish, the metal surface is covered with
rice husk.
- A ladle to tundish refractory tube ( known as shroud)
is used to further avoid reoxidation of metal from atmosphere and to obtain
clean steel.
- The metal flow pattern inside tundish plays an
important role for removal of deoxidation/ reoxidation products through
floatation, wall adhesion and agglomeration phenomenon, which in turn is a function
of tundish design / weirs or dams building in the tundish.
The
flow of molten steel between the tundish and moulds is controlled through monoblock
stoppers ( Use of slide gates for metal dispensing from multi nozzle tundish profoundly
raises repair and maintenance cost ).
Appearance of a 4 strand Bloom Tundish at the commencement of continuous
casting process.
One
operating panel box for casting is suspended beside each mould.
Submerged Entry Nozzles (SEN).
After attainlng smooth dispense of metal from
metering nozzles of a newly started tundish, the Submerged Entry Nozzles (SEN)
are sited to prevent metal re-oxidation from atmospheric oxygen to obtain clean
steel. An important function of Submerged Entry Nozzles is also to prevent
metal splash over mould walls and improve steel flow in the mould, avoid hot
faces on mould walls surface.
The submerged entry nozzle are preheated before putting to
casting process to eliminate the risk of freezing of metal in the nozzle at the
beginning of casting.
Mould
Powder / Flux:
The
surface of molten steel in the mould is covered by continuous feeding mould Powder (synthetic slag)
from the top of moulds.
The
mould flux plays essential role in continuous casting process and its main
functions are to provide:
-
Thermal
insulation of metal surface to prevent heat loss and avoid premature
solidification of liquid steel in the meniscus zone.
-
A
lubricating film to prevent adhesion of solidifying steel to the mould walls
and thus facilitates strand withdrawal.
-
Protection
of the molten steel from reacting with atmospheric oxygen.
-
Uniform
control of heat transfer between solidifying steel and mould to avoid surface
defects.
-
Absorption
and dissolution of non-metallic inclusions from the liquid steel, promotes the
cleanliness of finished steel products.
Mould
powder is constituted by a complex mix of Oxides mainly SiO2, CaO,
Na2O, Al2O3, MgO, fluorspar (CaF2)
and carbon. The chemical composition varies according to steel grades and
operational parameters of casting to achieve the required properties of uniform
melting temperature range, thermal conductivity, viscosity and surface tension.
Pakistan Steel produces it’s mould powders (slag forming compounds) for
internal use in steelmaking department.
Water
Cooled Moulds:
The main function of the mould is to establish a
solid shell of cast metal sufficient in strength to contain its liquid core
upon entry into the secondary spray cooling zone.
As
per projects the appearance of copper moulds for Bloom Casting machine, placed
over oscillating stand was as under.
The mould is basically an open-ended /bottomless
box, containing a water-cooled inner jacket made-up of a high purity copper
(99.99%) or copper alloy plates. Freezing
begins at the liquid steel meniscus level in the mould, forming a shell in
contact with the walls of water circulated copper mold.
Rate of cooling controls the solidification of metal and
determines the microstructures in casting sections, controls the size and shape
of the grains, segregation,and the distribution of inclusions and porosity.
Solidification is also critical to the hot-cracking behavior of metal.
Mould
Oscillation:
The moulds are oscillated up and down vertically via motor driven cams installed under casting floor to employ a stroke pattern ( called “ negative strip” ), in which the downward stroke of the cycle enables the mould to move down faster than the strand withdrawal speed which prevents metal skin adhering (sticking) to mould walls in its upper part, ( called meniscus area) and facilitates solidifying metal strand withdrawal from mould. The oscillation is auto-adjusted and varies in frequency as per the speed of continuous casting process.
Secondary Cooling Section:
Just below the moulds, the four
solidifying faces of Cast Blooms are typically supported with rollers of
secondary cooling section through which the partially solidified metal is to be
passed. A secondary cooling section is made up of several supporting roller
frames and a series of nozzles sections which spray air mist water at a
predetermined rate to further assist in solidifying the core of the strand.
Appearance of secondary cooling sections for Bloom caster.
Appearance of secondary cooling sections for Bloom caster.
Choosing the right combination of casting
speed and secondary cooling rate for a specific steel grade is of the utmost
importance. This choice influences many different parameters during casting and
is one of the key choices for getting a good quality cast.
The operator controls
the casting speed by potentiometer. The oscillation frequency, controlled by
PLC, is changed based on the casting speed. The electro-optical sensor captures
the casting speed signal and sends it to the PLC system. Then the PLC system
controls the pneumatic valve to open or close the secondary cooling water.
The water cooled moulds and
secondary cooling sections are encased in a bunker/ chamber from where the
process generated steam is expelled out throught exhaust ducts and blowers.
Bloom withdrawing guide rollers of radial portion of 4 –Strand Bloom Casting Machine at Steel Making Department Pakistan Steel.
Bloom withdrawing guide rollers of radial portion of 4 –Strand Bloom Casting Machine at Steel Making Department Pakistan Steel.
The solidifying blooms are withdrawn from the moulds
and secondary cooling zone by a set of rolls
which guide the steel strands through a radial portion (arc) until the strand
is horizontal.
Withdrawing
and straightening guide roller’s sections are the key parts of continuous
casting machine which are used to insert the dummy bar into the bottomless moulds
to initiate casting process, withdraw hot strands from the moulds, radial
section and straighten them with the dummy bars.
The
rolls are positioned close enough together to avoid bulging of the thin metal shell.
The bloom casting machine of Pakistan Steel is a mechanically strong machine.
The rollers of Bloom Continuous casting machine are fitted with slide bearings that require extensive lubrication. Improper lubrication leads to bearings failures, frequent break-outs, machine damage and loss of production time. A central greasing system is provided in the design to accomplish the task.
A view of straightening rollers of Bloom Casting Machine Steel Making Department Pakistan Steel.
The rollers of Bloom Continuous casting machine are fitted with slide bearings that require extensive lubrication. Improper lubrication leads to bearings failures, frequent break-outs, machine damage and loss of production time. A central greasing system is provided in the design to accomplish the task.
A view of straightening rollers of Bloom Casting Machine Steel Making Department Pakistan Steel.
Solidification
begins at the liquid steel meniscus level in the mould forming a shell in
contact with the walls of the water circulated copper mould and progressively
continues as the strand moves down through the casting machine in the secondary
cooling zone.
Choosing the right combination of casting speed and secondary cooling rate is of the utmost importance. This choice influences many different parameters during casting and is one of the key choices for getting a good quality cast. One parameter that is directly influenced by this choice is the metallurgical length.
The distance from the meniscus level to the point of complete solidification within the machine is called the metallurgical length.
Solidification of cast blooms is gradually completed as they reach to Dummy bar separating pinch rollers. Rate of cooling controls the solidification of metal and determines the microstructures in casting sections, controls the size and shape of the grains, segregation, and the distribution of inclusions and porosity. Solidification is also critical to the hot-cracking behavior of metal.
Pinch rollers for Dummy Bars separation and Dummy Bars
parking posts of 4-Strand Bloom Caster at steel making department Pakistan
Steel.
Pinch
rollers separate the dummy bars from initially cast blooms and direct the dummy
bars towards the parking posts and permit continuously cast stream of the solidified blooms towards the gas cutting flying torches.
Another
view of dummy bars parking posts and Gas cutting flying torches of 4-Strand
Bloom Continuous Casting Machine at Steel Making Department Pakistan Steel.
Flying
torches control the length of the blooms, synchronously cut the bloom's strands
into a pre-determined length and lets the casting process continued for one
hour to several hours.
A hot scarfing machine (French made) on the production line is
used for treating the surface defects such as flaws, de-carburized layers,
sharp corners and slag removal from the steel surface of continuously cast
blooms for satisfying the quality requirements before dispatching to stock
yard.
The Blooms are transported via electrically driven roller lines and trolley cars to the stockyard, where the blooms are stacked to their respective stocking area of Billet mill for their subsequent rolling into rolled billets.
The Blooms are transported via electrically driven roller lines and trolley cars to the stockyard, where the blooms are stacked to their respective stocking area of Billet mill for their subsequent rolling into rolled billets.
In
the designs of integrated steel mills especially of the epoch of 1970-80, the
Bloom continuous caster is typically decoupled with the rolling mills, meaning
that the Blooms are allowed to cool and are put into storage/stockyard.
When
an order of appropriate-size of billets is received, the blooms are reheated
before rolling to reduce the cross-section to required smaller sizes Billet in
Billet Rolling Mill.
Subsequently underneath of moulds, the continuously cast
billets are passed through the secondary cooling zone and radial portion of the
machine to attain complete solidification.
6 – Strand Billet Continuous Caster.
(Steel Making Department ) Pakistan Steel.
A six stand Billet Continuous Caster (Voestalpine
Austria made ) was added to Steel Making
Department in 1989
to maximize the efficiency of production capacity of long products,
including through the identification of possible synergies and to optimize the
production chain, such as in the holding across the production chain of steel
making department and long rolled products.
The continuous Billet caster casts square strands of
smaller cross-section that are used to produce materials for wire rod, bars,
shapes and pipe etc.
The cross- sectional sizes of continuously cast Billets
are as under:
150 x 150 mm.
125 x 125 mm.
100 x 100 mm.
80 x 80 mm.
The ladle turret holds the steel teeming ladles, each of
which weigh up to 130 tons. The Ladle turret rotates backward and forward into
casting and charging position and provides smooth rotation for accurate
positioning, starts and stops ladle over tundish to reduce tundish metal level
fluctuation and temperature drop.
One operating panel box is suspended beside each mould.
To initiate casting process, the electrically driven tundish car is moved to align
the metering nozzles of the tundish with the openings of water cooled copper
moulds.
A view of casting moulds and operating panel boxes of 6- strand
Billet caster ( steel making department) Pakistan Steel.
The parabolic tubular moulds (consist of a one‑piece
copper lining) are employed in billet continuous caster that are capable of
intensive heat extraction and high heat transfer efficiency.
The copper mould tubs work under high temperature
condition so their material must have high thermal conductivity, high strength,
sufficient wear resistance and hardness to obtain good life.
The moulds are moved up
and down (oscillated) to stop the metal shell from adhering to the moulds.
The parabolic tubular moulds are crucially important for
obtaining minimal clearance between the mould tube wall and continuous billets
crust, which while moving inside the copper tubes and under intensive cooling,
undergoes constant natural shrinkage and reduction of sections.
The molten steel is poured out of steel ladle through
slidegate into the tundish and after maintaining the required level of metal in
tundish, the molten steel is allowed to dispense into the moulds via metering
nozzles of the tundish.
An open metering nozzles system is employed in billet
caster tundish (distinct to mono block stoppers – metering nozzles system used
at Bloom continuous caster), producing silicon‑killed steel grades.
Metal discharge rate is controlled by the bore of the
nozzle and the ferro static pressure (metal height in
the tundish) above the nozzle. Different bores of metering nozzles are
selected depending on the section size cast and casting speed required.
The casting speed can be controlled within 0-4m/min
according to different steel grades and cross-sections of moulds. With highly
efficient cooling, steel billets with outer solid shell formed move out of the moulds.
Then the solidified
billet strands pass into guides that move them to the horizontal plane for
leaving the stand.
The dummy bars complete their task after extracting the
cast strands at the start of casting process, depart to the dummy bar storing
posts and park there till next series of casting operation is initiated.
A view of
secondary cooling water piping, dummy bar parking devices and gas cutting torches
of six strands Billet Caster at ( S.M.D ) Pakistan Steel.
The billets are cut to the required length by flame cutting torches
and are transferred to the billet cooling bed by tilting gear or lifting devices.
Appearance of
flying gas cutting torches of six strand Billet Continuous Caster in operation.
After cooling the cast billets are hoisted to the
appointed billet storing place in the premises of steel making department Pakistan
Steel for onward direct supply to rolling mills.
The
rolled and cast billets are supplied to rolling mills to get them rolled in
vast range of different shapes and sizes. Bars can have cross-sectional shapes
of squares, rectangles, circles, hexagons, angles. They can be re-rolled in
cross-sections shaped like an H or I (called joists, beams and columns), a U (channels)
or a T. These types of steel “sections” are used in modern civil construction.
Construction
is one of the world’s largest and most vital industries. From houses to
skyscrapers, schools, hospitals, ware-houses, factories, shopping centers,construction
also involves engineering projects including highways, bridges,
dams, dredging and nuclear power Plants.





























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.